It’s important to understand what is an EdD vs PhD before you can drill down into the individual programs and choose the course that’s right for you. Both doctorates are equivalent in level; however, there’s more than one difference between EdD and PhD when it comes to the nature and content of the degrees.
An EdD is an advanced degree focused on developing practical skills, while a PhD is centered around theory-based research.
Let’s start by examining both types of doctorate degrees in detail.
What Does EdD Stand For & What Is an EdD Degree?
EdD is short for “Doctor of Education.” An EdD typically involves practical research, participation in workshops, and other advanced practical skills. For instance, as part of your studies, you may have to implement a new program and submit its findings to your supervisor.
The subject of study depends on the specialty you choose. For example, you may pursue an EdD in finding the best educational practices. This could involve spending time in a range of classrooms to understand the current education system and identify innovations that may be valuable.
Experts recommend an EdD for education professionals who want to drive change in the current educational system. Candidates for a Doctor of Education include education professionals from a diverse range of fields, from teachers of K-12 students to educators working in government and military settings.
Generally speaking, an EdD is designed to give you skills and knowledge that you can easily apply to a real-world environment. This is a high-level, complex degree that goes far beyond research. Students will not only research their specific area of interest, but they will also apply this research to their work and community to drive decision-making and innovation in the real world.
What Can You Do With an EdD Degree?
EdD programs are designed to prepare students for leadership roles in the education sector, where they can apply their learning and research to improve learning outcomes and the sector in general. While these programs focus on the educational sector, they have a broad scope and can be applied to other industries, not just education.
Most EdD graduates manage or lead schools, universities, colleges, and other advanced educational institutions. Other roles may include training teachers, driving innovative change in educational approaches, and performing research in their respective fields.
Here are some other roles that you may secure thanks to an EdD qualification:
● Postsecondary Education Administrator: These administrators work in universities and colleges to manage admissions, student affairs, and the institution in general. These professionals may hold the title of dean, vice president, and president of the school. The average salary of a postsecondary education administrator is around $46.87 per hour or $97,500 per year.
● Elementary School Administrator:These professionals are in charge of staffing and general management of elementary schools.
● Top Executives: Executives are responsible for developing business plans and strategies that can help organizations in the education sector meet their goals. They also oversee academic performance, school programs, and other institutional tasks.
● Coordinators: Coordinators manage the curricula and other educational matters at elementary schools, secondary schools, and colleges. A coordinator helps tutors to apply effective teaching strategies while managing the overall effectiveness of programs.
These are just a few of the many career opportunities for EdD graduates.
What Is a PhD?
A PhD is a doctoral degree for students who want to pursue theory-based research in their area of specialization. As opposed to an EdD, a PhD typically has a more theory-based approach to education. The goal is to master a particular subject or improve on sting research by adding unique findings.
This degree is best suited to those who wish to become academics, whether in the fields of research or teaching. As part of completing a PhD program, students often publish their work in reputed journals and present at national conferences, helping to further their academic careers.
What Can You Do With a PhD?
A PhD opens up a range of career opportunities. You can start working as an assistant professor while completing your PhD, or work as a full-time professor, researcher, or school administrator after graduation.
After completing a PhD, most graduates secure roles in one of two main areas:
- Postsecondary Teachers: PhD graduates are qualified to teach at a university level. When postsecondary teachers are not teaching, they attend conferences and work on academic papers. A postsecondary teacher can make up to $80,560 a year, according to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics.
- Academic Researcher: Research, both within universities and for private institutions, is another common career pathway for PhD holders. Academic researcher salaries vary depending on the area of specialty, type of research, and amount of time invested in the research.
PhD vs EdD: Key Differences
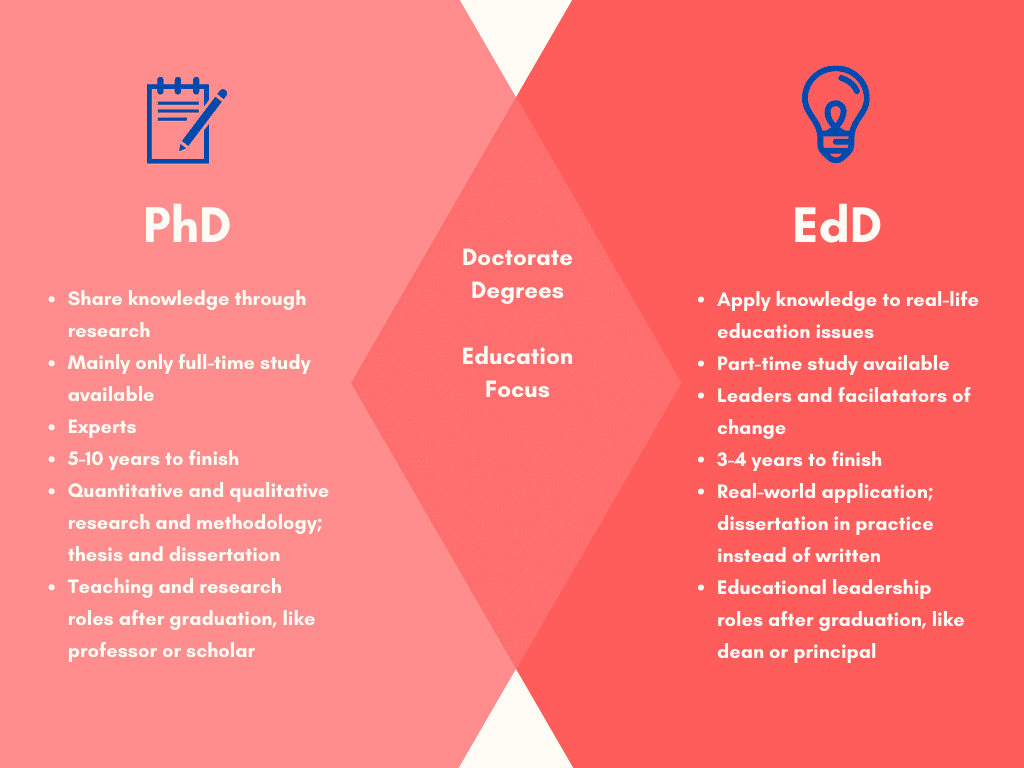
Both a PhD and an EdD are doctorate degrees, but each type of degree has a different academic environment and different associated career paths. If you are interested in pursuing a career in academia, a PhD is your best bet. This degree focuses on theory-based research and equips you to become a university professor or academic researcher.
On the other hand, if you’re interested in a leadership role in the education sector, a Doctorate in Education is probably the best option for you. This kind of degree is most suitable for candidates who want to pursue leadership roles in colleges, universities, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. Armed with an EdD degree, you can also become a trainer or an instructor across a range of industries.
Here are a few key differences between an EdD and PhD in education:
● An EdD typically requires only 60 units of credits while a PhD usually needs 90 credits, depending on the program.
● An EdD takes around three years to complete full time. A PhD, on the other hand, can take from three years to five years, or even more, depending on the field you choose.
● An EdD is a largely practical course, while a PhD is a research-based program that typically focuses on theoretical concepts.
PhD Versus EdD – Career Opportunities
Generally speaking, an EdD will help you to secure a leadership role in the education sector, while a PhD opens up career opportunities in research and academia.
A PhD can help you pursue a career as a:
- School curriculum coordinator
- Professor or assistant professor
- Academic researcher
- Educational consultant
An EdD can help you become a:
- School or college leader
- Policymaker
- Decision maker
- Curriculum developer
These are just a few of the potential career directions, with a wealth of career opportunities available for students who complete either of these types of doctorate programs.
FAQs
Is a PhD Better Than an EdD?
A PhD and an EdD are equivalent in level. However, they do support different career paths. A PhD is more valuable if you’re seeking a career in academia.
Can an EdD be called a Doctor?
Yes, absolutely! An EdD is a doctorate degree and graduates earn the title of Doctor. An EdD refers to a Doctor of Education, so yes, you will be called a doctor after completing this program.
Can You Be a Professor With an EdD?
Yes. Once you have completed your EdD degree, you will be qualified to teach students at a post-secondary level, for example, at a university or college. Many universities hire professors and assistant professors with an EdD degree, though it is more common for academic teaching and research staff to have a PhD.
Final Thoughts
When it comes to an EdD vs PhD in Education, both are high-level, valuable degrees that open up a range of career opportunities in the education sector. When deciding between an EdD or PhD, remember the key differences. An EdD has a more practical focus, and is designed to help you become an education leader or policymaker. On the other hand, a PhD is largely based around theoretical research and will allow you to become a university professor or academic researcher.
For more choosing the right advanced degree for you, take a look at our guide to master’s and PhD timelines, as well as our round-up of the top 20 online PhD programs.
Lisa is a full-time writer specializing in career advice, further education, and personal development. She works from all over the world, and when not writing you'll find her hiking, practicing yoga, or enjoying a glass of Malbec.











